The muscles found between your ribs are called intercostal muscles. Together with other chest muscles, the internal and external intercostal muscles allow movement and stabilize your chess wall. However, they can be strained during sports or other conditions when sudden twisting of upper body occurs. Read this article for full understanding of intercostal muscles and its strain.
What Are Intercostal Muscles?
We often think of muscles as large, bulky masses of tissue, but the intercostal muscles are actually thin muscles in the chest.
Location
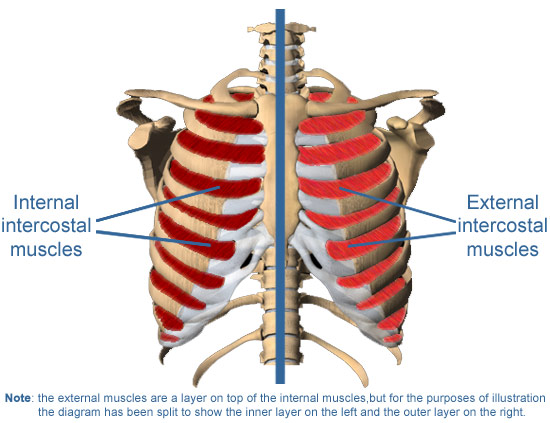
The intercostal muscles are thin bands of muscles located between ribs. There are two types of intercostal muscles: the internal and the external intercostal muscles. These muscles have blood vessels and nerves, which are also found in the intercostal space between ribs.
Function
The intercostal muscles contract during inhalation or deep inspiration to support breathing. The external intercostal muscles contract and elevate the ribs during inspiration while the internal and subcostal (innermost) muscles lower your ribs during forced exhalation.
Intercostal Muscle Strain
Symptoms
Symptoms of intercostal muscle strain may consist of a sharp, stabbing pain during breathing or a persistent soreness or ache in the ribcage. Pain is usually worse when deep breathing, or when you twist or bend sideways. Your disability and rate of recovery depends on the muscle strain grading, which indicates the degree of injury involved. The degree of muscle strain is classified into three grades:
1. Grade I consists of a mild muscle strain where only some muscle fibers are damaged. Healing time takes about two to three weeks.
2. Grade II consists of a moderate muscle strain where more muscle fibers are involved, but muscles are not ruptured. Healing time takes three to six weeks.
3. Grade III involves severe injury and complete rupture of the muscle. Surgical repair is required to heal the muscle. Healing may take up to three months.
Causes
1. Twist Body. Muscle strains usually occur when the muscle or its tendon is suddenly stretched or pulled. Intercostal muscles may be strained when you experience forceful or exaggerated twisting of the torso or when you swing your arms forcefully.
2. Sports. Activities that often result in intercostal muscle strains include racquet sports, golf, and baseball. Direct blows to the ribcage (ex. during football tackles) may also lead to stretching of the intercostal muscles, resulting in muscle strain.
Home Remedies
1. Relax. The best way to relieve symptoms of muscle strain is to rest and stop your sports activity. You must also limit torso movements to prevent further injury to the muscles. Take a complete bed rest but not more than two days. Prolonged inactivity may lead to muscle tightness and reduced trunk flexibility, which may delay healing.
2. Apply Ice Pack. Use an ice pack wrapped in towel and apply it on the injury for 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times daily, for two days following injury. You may continue this until swelling and pain subside.
3. Take Painkiller. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be taken to relieve pain. You may also ask your doctor for a prescription if needed.
4. Take Exercises. Exercising can help in the healing process and strengthen your injured muscles. Try some of these:
- Deep Breathing
- Rotation when Lying
- Foam Roller Stretch.
To begin, sit or stand with your neck and back straight. Breathe in (inhale) as deeply as you can without increasing pain and then slowly exhale. Make sure you focus on inhaling using only the lungs, without elevating the shoulders. You will note that your stomach will gently expand. Repeat this 5 times.
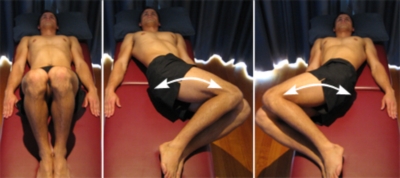
To begin, lie on your back with knees bent. Slowly rotate your knees side to side as far as you can, without causing pain. Repeat this 10 times.
Using a foam roller under the upper back, relax and breathe normally. Stay in this position for 15 to 90 seconds as long as comfortable and without pain. You may also take your arms overhead.