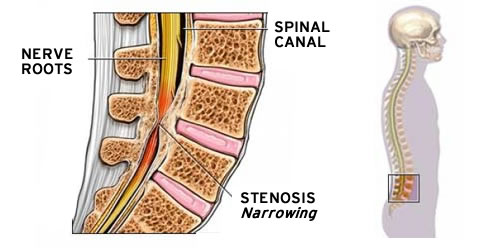
Even though the term stenosis comes from the Greek meaning choking, spinal stenosis has quite little in common with choking. Spinal stenosisdoes cause a narrowing of your spine. This narrowing makes pressure on your spinal cord and nerves, likely causing pain. It happens usually in people over the age of fifty. People who are younger and have a spine injury or a narrow spinal canal can also be at risk.
What Is Spinal Stenosis?
A narrowing of the spaces in the spine or backbone is called spinal stenosis, resulting in pressure being put on the nerve roots and/or the spinal cord itself. This is a disorder which usually involves the narrowing of one or more of the three areas found in the spine: (1) the canal found in the center of the column of bones (spinal or vertebral column) through which the nerve roots and spinal cord run, (2) the canals found at the roots or base of the nerves that branch out from the spinal cord, or (3) the openings found between the vertebrae or spinal bones, through which the nerves leave the spine and travel to other parts of the body. This narrowing can involve a large or small area of the spine. Pressure on the nerve roots or lower part of the spinal cord could cause numbness or pain in the legs. Pressure on the top part of the spinal cord or neck area could make similar symptoms in the shoulders or perhaps the legs.
What Are the Types of Spinal Stenosis?
There are two kinds of spinal stenosis: cervical stenosis and lumbar stenosis. The most common one is lumbar stenosis. However, cervical stenosis is much more dangerous.
1. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Here, the spinal nerve roots found in the area of the lower back are choked or compressed, which could make symptoms of sciatica including weakness, tingling or numbness which radiates from the lower back to the buttocks and legs. The symptoms will be more serious with activity.
2. Cervical Spinal Stenosis
This pain found in the neck is possibly more dangerous because it compresses the spinal cord. It can lead to serious symptoms like paralysis or major body weakness. However, these symptoms of spinal stenosis are practically impossible in the lumbar spine since the spinal cord is not in the lumbar spine.
What Causes Spinal Stenosis?
Some people are actually born with a small spinal canal, but most cases of spinal stenosis happen because something happens to reduce the space available in the spine. Spinal stenosis causes usually include:
1. Bone Overgrowth
Normal wear and tear on the bones in your spine can cause bone spurs to form, which can grow into the spinal canal. A bone disease which generally affects adults, Paget’s disease, can also cause overgrowth of the bone in the spine.
2. Herniated Disks
The soft cushions which act as shock absorbers between your vertebrae generally dry out as they age. Cracks in the exterior of the disks can let some of the soft material inside to escape and press onto the nerves or spinal cord.
3. Thickened Ligaments
The cords which help hold the bones of your spine together are tough, and can get stiff and thicken over time. These thickened ligaments can bulge into your spinal cord.
4. Tumors
Growths which are abnormal can form in the membranes which cover the spinal cord or inside the space between the vertebrae and spinal cord.
5. Injuries to the Spine
Major trauma such as car accidents can create fractures or dislocations from one or more vertebrae. The displace bone could damage the contents of the spinal canal. Adjacent tissue becoming swelled right after back surgery can also put pressure on the nerves or spinal cord.
How to Treat Spinal Stenosis
The kind of treatment you get for spinal stenosis can vary, depending on where the stenosis is and how severe your symptoms and signs are.
1. Medication
Your doctor can prescribe different medications depending on your pain.
|
Medications |
How They Work |
|
NSAIDs |
These nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help to lower inflammation and lessen pain. Some such as naproxen and ibuprofen can be obtained without a prescription. |
|
Muscle relaxants |
Medications like cyclobenzaprine can calm muscle spasms which will occur sometimes with spinal stenosis. |
|
Antidepressants |
Nightly doses of tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline can help relieve chronic pain. |
|
Anti-seizure drugs |
Some of these drugs like pregabalin and gabapentin can be used to lower pain caused by nerves which have been damaged. |
|
Opioids |
Drugs like oxycodone and hydrocodone have substances like codeine which can relieve pain, however, it can be habit-forming. |
2. Therapy
You can be taught exercises by a physical therapist to assist with:
- Building your strength up and endurance.
- Maintaining the stability and flexibility of your spine.
- Improving your balance.
In the video below there are some exercises you can follow which are great for people who suffer from stenosis spine:
3. Steroid Injections
It can help to lower the inflammation and take away some of the pressure by injecting a corticosteroid into the space around the constriction. Repeated steroid injections, however, can weaken nearby bones and connective tissue, so just a few injections per year are suitable.
4. Surgery
You should try surgery if:
- Other treatments that are more conservative have not helped.
- Your symptoms have disabled you.
- You are in good health.
The end goal is to take any pressure on your spinal cord or nerve roots away. A laminectomy, for example, takes away the back part of the vertebra that is affect and makes more room in the spinal canal. Vertebrae in some instances could need to be fused to keep the strength of the spine.
Surgery helps lower spinal stenosis symptoms in most cases. However, some symptoms will stay the same or worsen after surgery is performed. Risks from surgery can include a tear in the membrane which covers the spinal cord, infection, neurological deterioration and a blood clot in a leg vein.